Table of Contents
website
| Hong Kong Housing Authority Website | https://www.housingauthority.gov.hk/tc/index.html |
| Hong Kong Housing Society Website | https://www.hkhs.com |
| Institution Name | Year of establishment | Relations with the government | Main Responsibilities |
| Hong Kong Housing Authority (HA) Hong Kong Housing Authority | 1973 | A government statutory body, but not a government department | (1) Formulate long-term development strategies for public housing (public housing and Home Ownership Scheme housing). (2) Planned annual supply of public housing and home ownership housing Approving the planning, design and allocation policies for public housing. (3) To supervise the work of the Housing Department and ensure the effective implementation of its policies. Manage the financial resources of public housing (such as rent, property sales income, etc.). |
| Hong Kong Housing Department (HD) Housing Department | 1973 (Merged from the Resettlement Department and the Building Department) | A government department under the Housing Bureau | (1) Implementation of HA’s decisions (2) Responsible for the construction, maintenance, allocation and daily management of public housing. (3) Processing public housing applications, allocation of units and rental management. Overseeing construction works (such as new public housing projects). (4) Maintaining existing public housing facilities (e.g. building safety and environmental hygiene). (5) Crack down on the abuse of public housing resources (such as illegal subletting). |
| Hong Kong Housing Society (HKHS) Hong Kong Housing Society | 1948 | An independent non-governmental, non-profit statutory body, but funded and commissioned by the Government. | (1) Providing “sandwich class” housing (such as sandwich houses, elderly housing, etc.) to fill the gap in government public housing. (2) Manage its own rental housing estates (e.g. some of the earlier built public housing estates). (3) Promote urban renewal and sustainable community development projects. |
The threeDifferences in housing application
| project | Housing Authority / Housing Department | Housing Society |
|---|---|---|
| nature | Government Statutory Bodies/Departments | Non-profit non-profit organization |
| Main Services | Public housing, Home ownership housing | Sandwich houses, elderly houses, and designated rental housing villages |
| Income Limits | Strict (for grassroots) | More relaxed (for the middle class) |
| Operational Model | Direct government funding and management | Government commissioned project, partially self-financing |
| Application System | Integration with government systems | Independent application channel |
Relationship between the Hong Kong Housing Authority (HA) and the Hong Kong Housing Department (HD)
- Division of Labor: The Housing Authority is the decision-making body, responsible for policy formulation and supervision; the Housing Department is the executive body, responsible for implementing specific work.
- Cooperation Model:The Housing Department is required to report its work progress to the Housing Authority, and the Housing Authority relies on the Housing Department’s professional advice to adjust its policies.
- Financial independence: The Housing Authority has independent finances (mainly from rental and home ownership flat sales), but the Housing Department's operations are funded by government grants.
Example
- Policy Development:The Housing Authority decides on the "public housing rent adjustment mechanism", and the Housing Department is responsible for calculating the rent and notifying tenants.
- Project Construction:The Housing Authority approves the new public housing development plan, and the Housing Department is responsible for bidding and supervising the project.
- Daily Management:The Housing Department handles the eligibility review of public housing applicants, while the Housing Authority sets the application eligibility criteria.
- Housing Authority = Policy Makers + Supervisors
- Housing Department = Policy implementer + manager
Together, the two constitute the "decision-making-implementation" framework of Hong Kong's public housing system, ensuring the effective allocation and sustainable development of public housing resources.
Hong Kong Housing Society (HKHS)
- nature: An independent non-governmental, non-profit organization (established in 1948), but funded and commissioned by the government.
- Functions:
- Providing "sandwich class" housing (such as sandwich houses, elderly housing, etc.) to fill the gap in government public housing.
- Managing self-owned rental housing estates (e.g. some older public housing estates).
- Promote urban renewal and sustainable community development projects.
- Features:
- The operation is more flexible and some application qualifications can be customized (such as the income limit is slightly higher than the Housing Authority's standard).
- Some projects operate on a "self-financing" basis, with funding sources including low-interest government loans and rental income.
- It has a long history and had already assumed the role of public housing before the establishment of the Government Housing Authority.
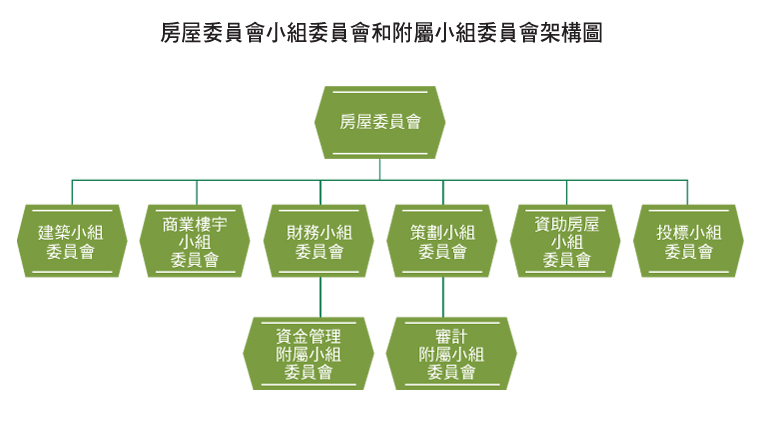
Hong Kong Housing Authority Organisation Chart
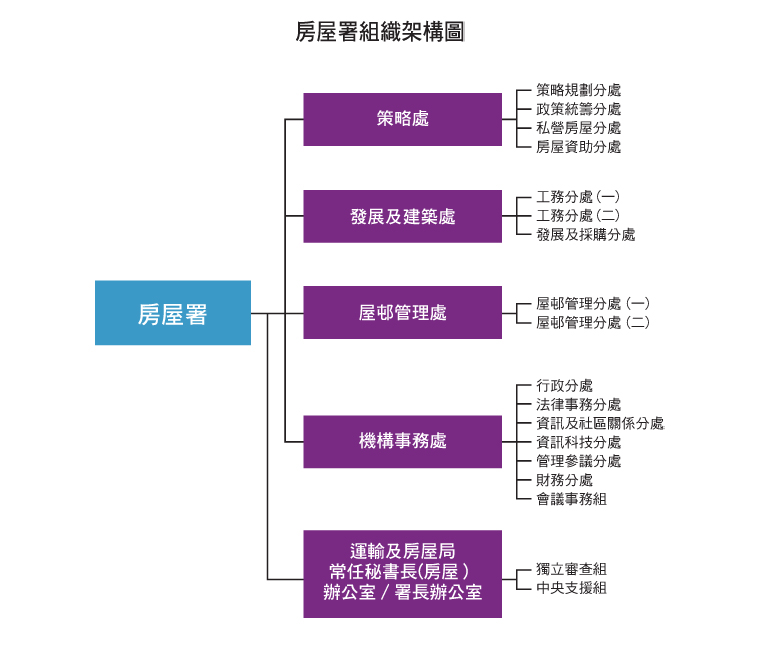
Housing Department Organisation Chart